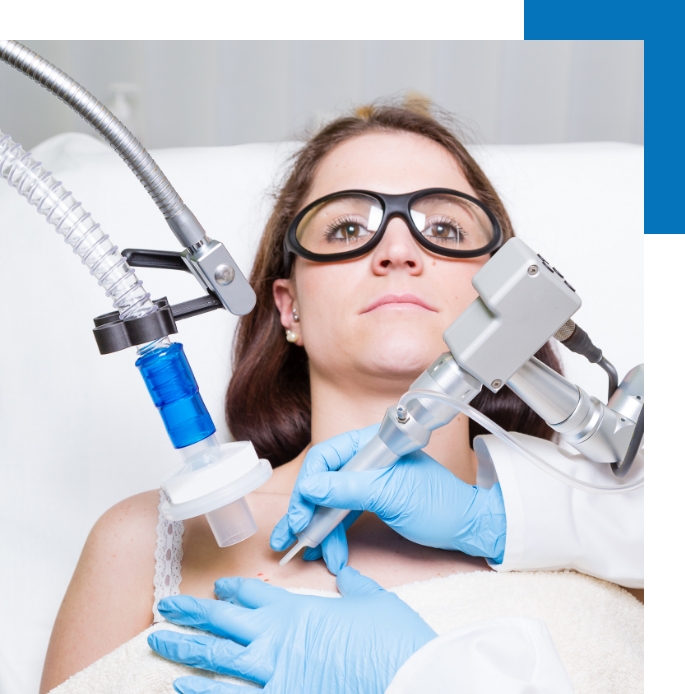
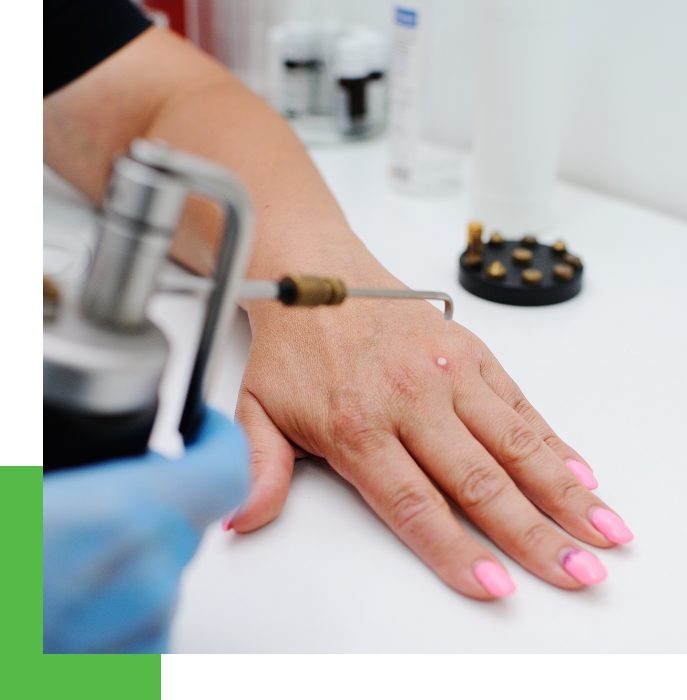
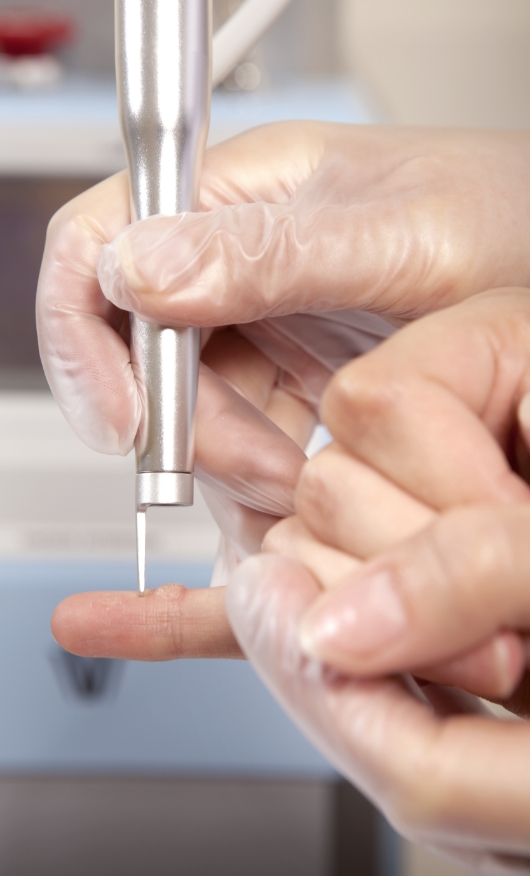
Under the patient is a plastic-coated ground plate or antenna. The "patient electrode" has the appearance of a circular loop and is retained by the operating surgeon. Lesion types necessitate specific electrodes, such as fine needle electrodes, wire loop electrodes, scalpel blade electrodes, etc.
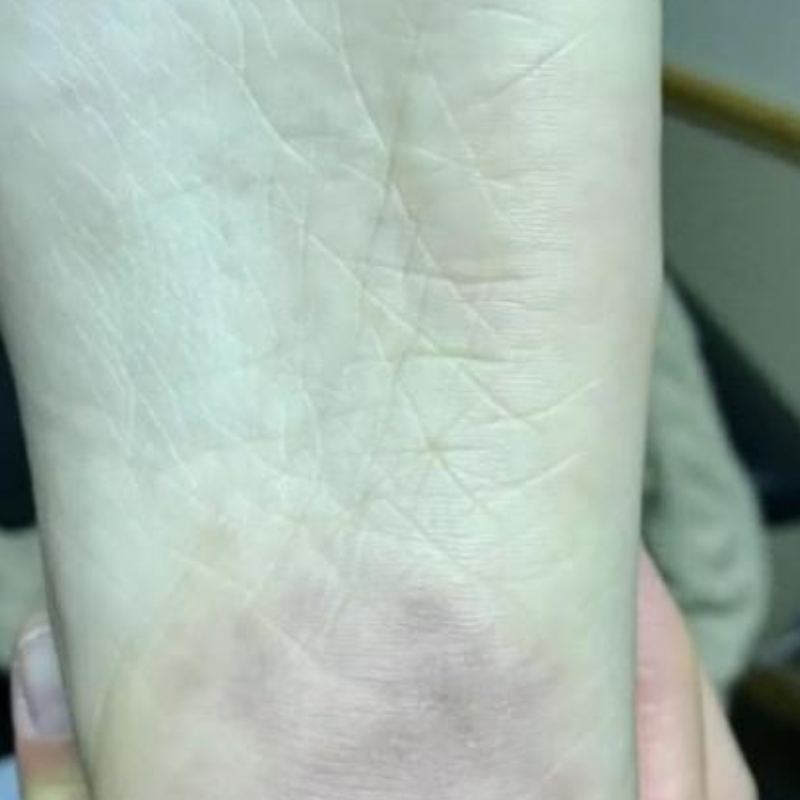
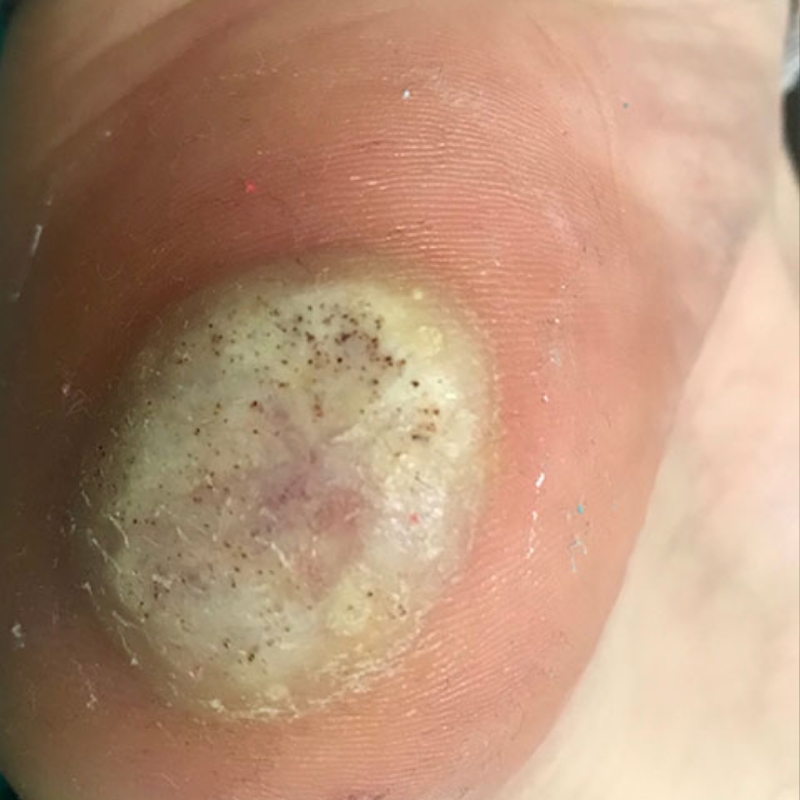
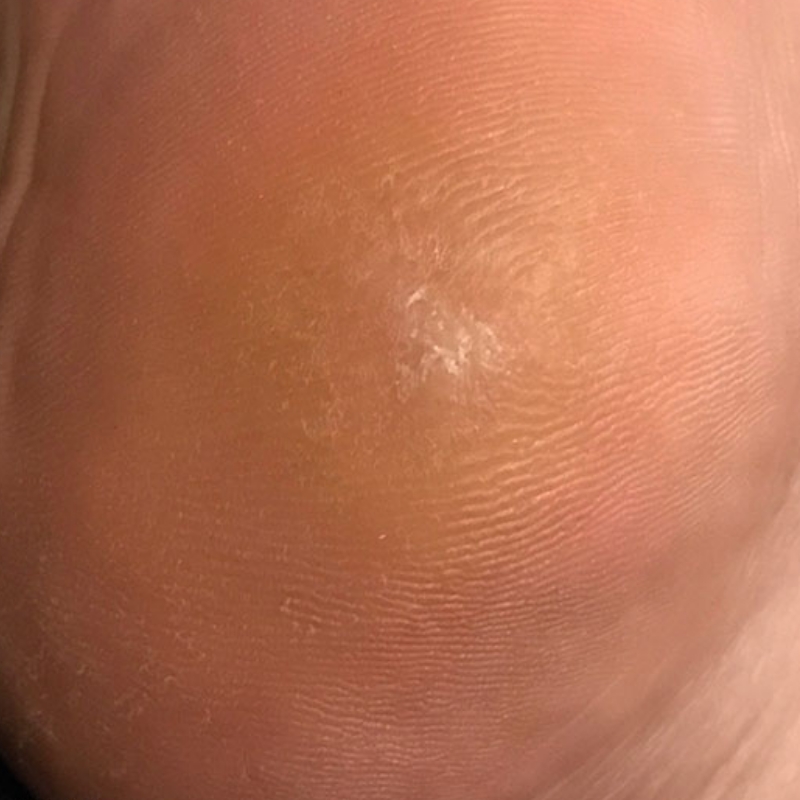
The electrode's tip needs to make contact with the lesion. When compared to traditional electro-cautery, it produces a negligible amount of heat. Due to the low level of collateral damage, the resulting wounds will heal more quickly and leave less scarring. Electrode tips transmit radio waves to the lesion, returning to the unit via the ground plate.
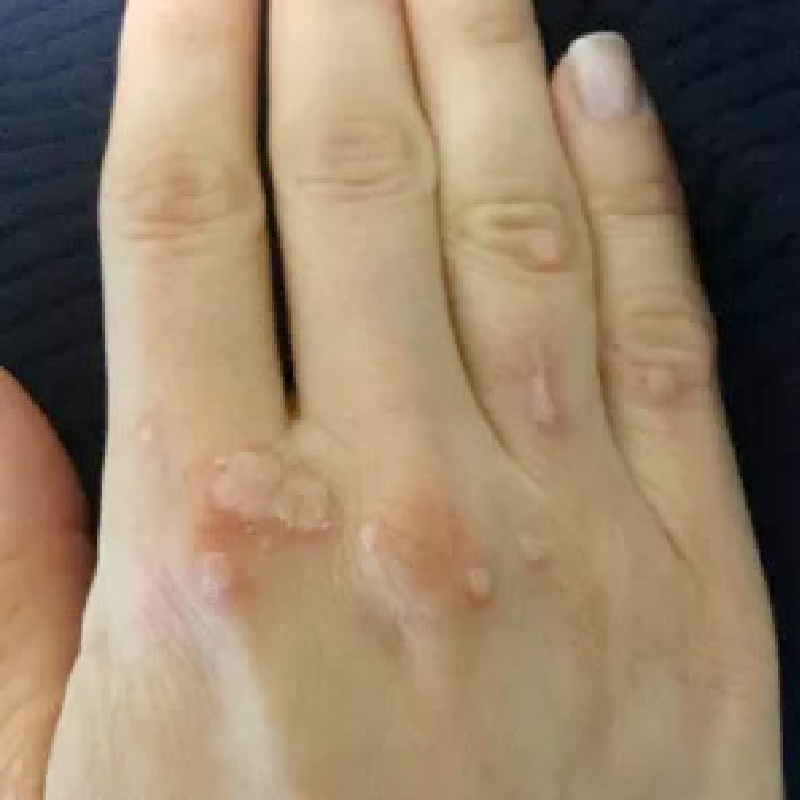
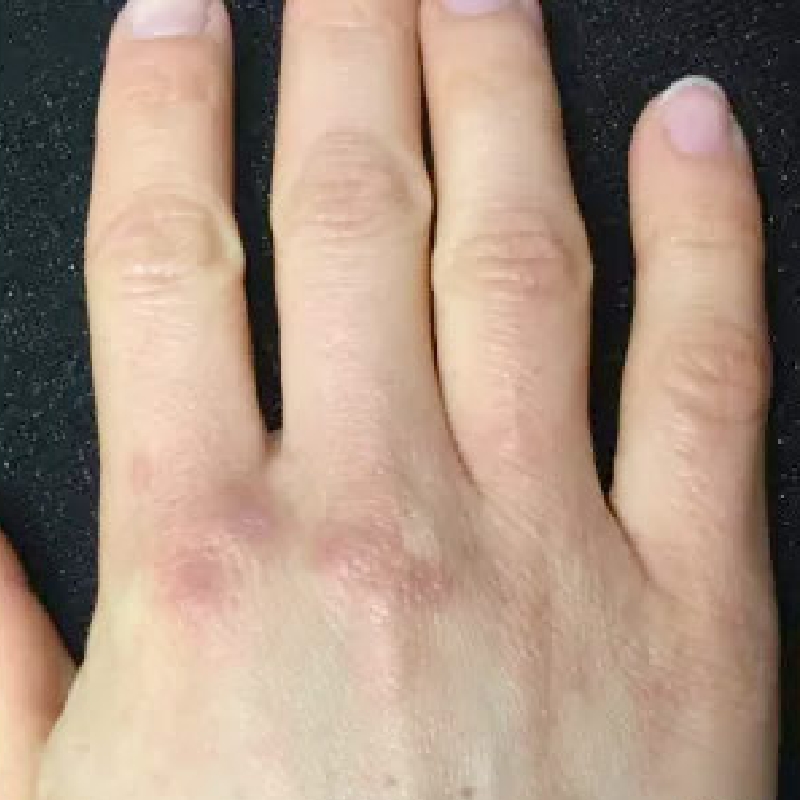
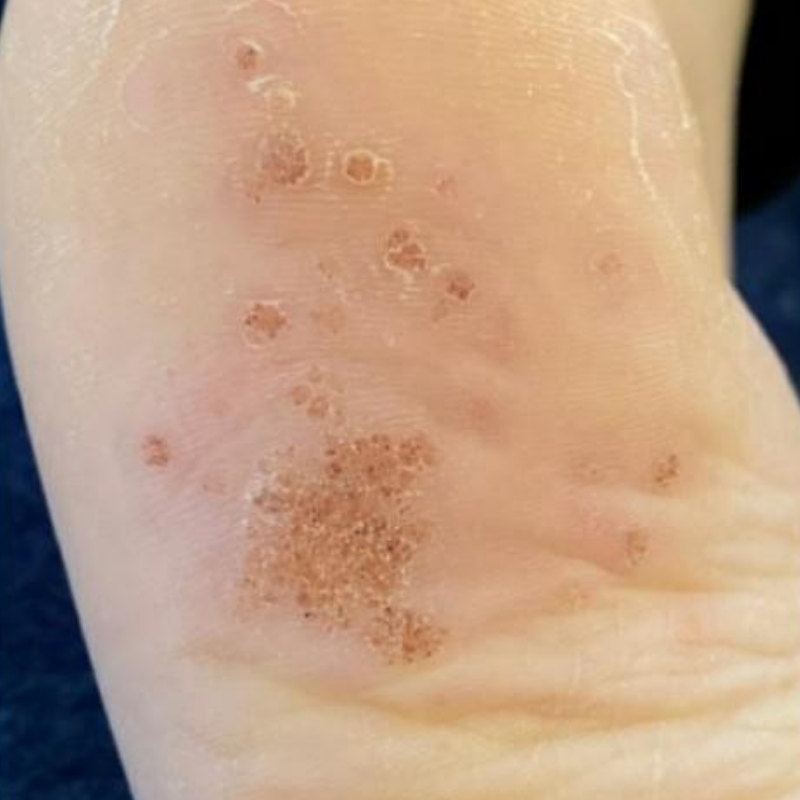
The patient's cells are vaporised, and the tissues are divided due to the release of energy caused by radio waves passing between the ground plate and the electrode. This energy is centred at the electrode end. When high-frequency wave encounter some resistance from the tissue, that resistance converts into heat. Boiling intracellular water raises intracellular strain to the point where the cell ruptures from the inside out. This is referred to as "cellular volatilisation".